 Sleep Apnea
Sleep Apnea
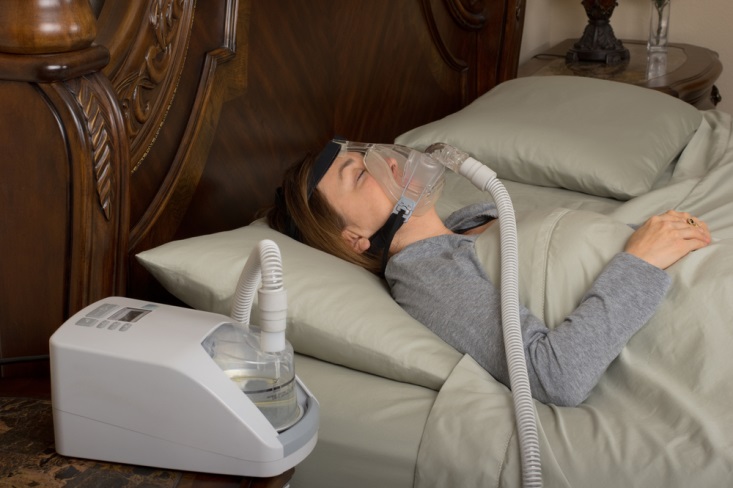
Complete cessation of breathing is known as apnea while hypopnea is partial cessation of breathing. Severity is determined by overnight polysomnography (sleep study or PSG). Success of treatment is documented by follow up PSG. Dangers associated with untreated sleep apnea include hypertension, lung damage, right heart failure, and heart rhythm irregularities. It may exacerbate the mortality risk of co-existing cardiovascular disorders.
Rating for Obstructive Sleep Apnea is determined by the severity of the disease as measured by the number of apnea and hypopnea episodes per hour and by the degree of hypoxia (low blood oxygen level). Favorable features include mild disease (low AHI and minimal hypoxia), consistent use of CPAP/BiPAP, controlled blood pressure, no risky driving events, and no co-existing heart or lung disease. Favorable cases are generally not rated.
Complete and eSubmit below
VERY IMPORTANT!!! If you don’t get the Success!!! notification after hitting submit, please scroll down to complete the missing requirements.
